Radius of Gyration in Structural Engineering
Radius of gyration describes the distribution of cross sectional area in columns around their centroidal axis.
In structural engineering the Radius of Gyration is used to describe the distribution of cross sectional area in a column around its centroidal axis.
The structural engineering radius of gyration can be expressed as
r = (I / A)1/2 (1)
where
r = radius of gyration (m, mm, ft, in...)
I = Area Moment Of Inertia (m4, mm4, ft4, in4..)
A = cross sectional area (m2, mm2, ft2, in2...)
Some typical Sections and their Radius of Gyration
Rectangle - with axis in center

Radius of Gyration for a rectangle with axis in center can be calculated as
rmax = 0.289 h (1)
where
rmax = max radius of gyration (strong axis moment of inertia)
Rectangle - with excentric axis
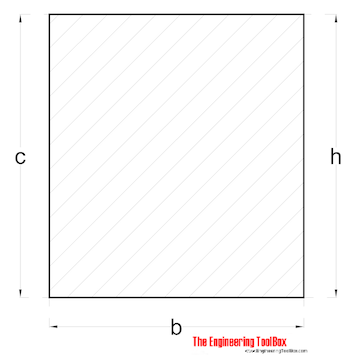
Radius of Gyration for a rectangle with excentric axis can be calculated as
r = 0.577 h (2)
Rectangle - with tilted axis
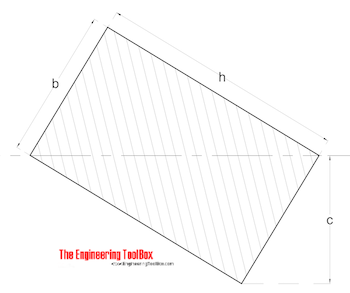
Radius of Gyration for a rectangle with tilted axis can be calculated as
r = b h / (6 (b2 + h2))1/2 (3)
Rectangle - with tilted axis II
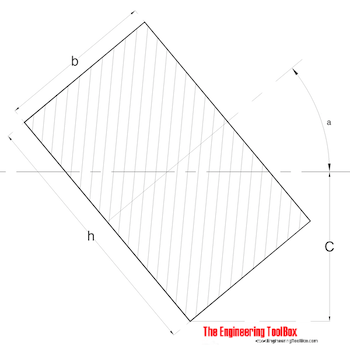
Radius of Gyration for a rectangle with tilted axis can be calculated as
r = (((h2 + cos2(a)) + (b2 sin2(a))) / 12)1/2 (4)
Hollow Square
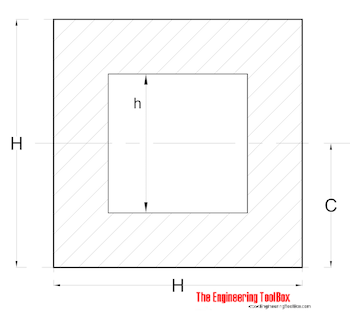
Radius of Gyration for a hollow square can be calculated as
r = ((H2 + h2) / 12)1/2 (5)
Hollow Square - with tilted axis
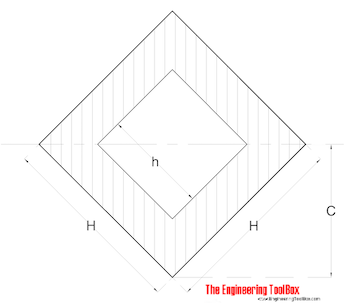
Radius of Gyration for a hollow square with tilted axis can be calculated as
r = ((H2 + h2) / 12)1/2 (6)
Equilateral Triangle with excentric axis
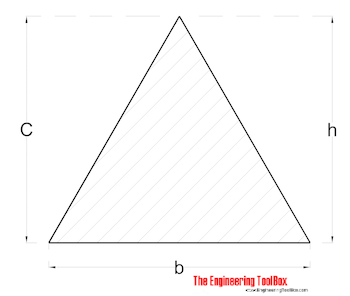
Radius of Gyration for a equilateral triangle can be calculated as
r = h / (18)1/2 (7)
Triangle
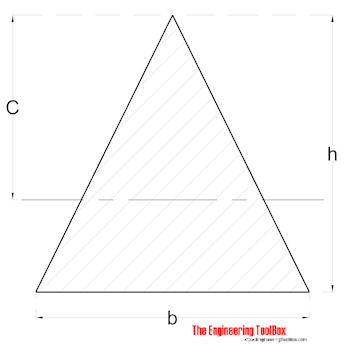
Radius of Gyration for a equilateral triangle can be calculated as
r = h / (6)1/2 (8)



