Fans - Volume Flow, Pressure Head and Power Consumption vs. Air Temperature and Density
The temperature and density of the air influences on the volume flow, pressure head and power consumption in a fan.
Density of air varies with temperature and pressure (or altitude or elevation above sea level) and a fan will not deliver according manufactured specifications if operating conditions are outside NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure Conditions.
NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure Conditions
Manufactured specifications for fans are in general based on the
- NTP - Normal Temperature and Pressure Conditions - 20 oC, 101.325 kN/m2, 1.204 kg/m3 (68 oF, 29.92 inches Hg, 0.075 pounds per cubic foot).
A fan is a "constant volume" device where the volume in the fan - and the transported air volume through the fan - is always the same (with same fan speed and size).
Since the density of air varies with temperature and pressure the mass flow through a fan varies with temperature and pressure.
- hotter air and lower air density - less mass will be transported through the fan
- colder air and higher air density - more mass will be transported through the fan
- equal speed and dimensions - the volume flow remains equal
When selecting a fan it is important to know if the specification of the system is based on operating conditions or NTP conditions. The formulas below can be used to calculate the volume flow, pressure head and power consumption at NTP conditions if the operating conditions are known, or vice versa if the NTP conditions are known.
The examples below may clarify the procedures:
Operating Volume Flow vs. Reference Volume Flow
Note! - the volume flow through a fan is constant as long as the physical dimensions and the speed of the fan are not changed. The amount of air (mass) passing through the fan varies with the air density and the air density depends on the temperature (as long as the pressure is constant).
If you have the required volume flow for a fan at a reference condition (typical NTP) - the operating volume volume flow for the fan at other operating temperatures can be calculated as
qo / qr = (273 + to) / (273 + tr) (1)
or
qo = qr (273 + to) / (273 + tr) (1b)
where
qr = reference volume flow (m3/s) - in general NTP conditions
q o = operating volume flow (m3/s)
tr = reference temperature (oC) - in general 20 oC NTP conditions
to = operating temperature (oC)
Example - Required Fan Volume Capacity
A drying process requires 1 m3/s air at normal conditions 20 oC . The fan operates when the air is heated to 80 oC . The required volume capacity in the fan at operating conditions can be calculated using 1b as
qo = (1 m3/s) (273 + (80 oC)) / (273 + (20 oC))
= 1.2 m3/s
The fan must be selected for volume flow 1.2 m3/s (and whatever the pressure loss in the system is).
Pressure Head
The ratio between developed pressure at different temperatures can be expressed as:
dpo / dpr = (273 + to) / (273 + tr) (2)
or
dpo = dpr (273 + to) / (273 + tr) (2b)
where
dpr = reference pressure developed (Pa) - in general at NTP conditions
dpo = operating pressure developed (Pa)
With temperature higher than the reference temperature - the volume flow is higher and the required pressure developed in the fan is higher.
Power
The ratio between power consumption at different temperatures can be expressed as:
Po / Pr = (273 + tr) / (273 + to) (3)
or
Po = Pr (273 + tr) / (273 + to) (3b)
where
Pr = reference power consumption (W)
Po = operating power consumption (W)
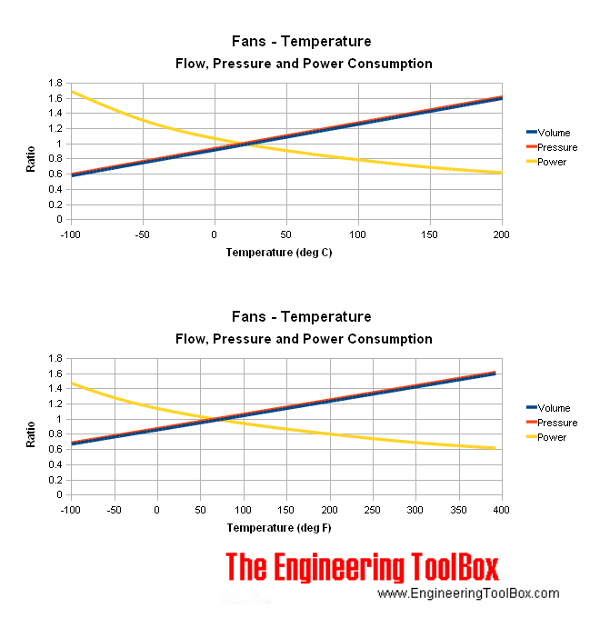
Volume, Pressure and Power Ratio Chart
The volume, pressure and power ratios are expressed in the chart below. The chart is based on a NTP reference with temperature of 20 oC .
Volume, Pressure and Power Ratios Calculator
The calculator below can be used to estimate the volume, pressure and power ratios at different temperatures. The default values are based on NTP conditions.
Example - Fan with Hot Air
A fan delivers 10000 m3/h of hot air at 60 oC. The total pressure loss in the system at this volume is estimated to 500 Pa .
Decide the correct air volume and pressure for choosing a fan from the manufacturers data. Decide the power consumption.
Since the air volume is estimated for the hot air, the correct volume for the fan is 10000 m3/h .
The pressure coefficient is approximately 1.15 for air at 60 oC according the chart. The correct pressure in the manufacturing data sheet should be
500 x 1.15
= 575 Pa
The power consumption according the manufacturing data is 2.5 kW. The power coefficient is approximately 0.88 for air at 60 oC according the chart. The correct power consumption should be
2.5 kW x 0.88
= 2.2 kW
Note! - do not compensate the pressure developed by the fan if the pressure loss in the system is estimated on the basis of normal charts based on air with density 1.2 kg/m3.
Example - Fan with Combustion Air
10000 m3/h of normal standard air at 20 oC shall be transported at an operating combustion air temperature of 180 oC. The total pressure developed at 180 oC is estimated to 500 Pa .
Decide the correct air volume and pressure for choosing the fan from the manufacturers data and decide the total pressure for selecting the fan!
The volume coefficient in the chart above is 1.55 at 180 oC. The operating volume flow for selecting the fan would be
10000 × 1.55
= 15500 m3/h
The pressure coefficient for air at 180 oC is approximately 1.55 according the chart. The developed pressure with normal standard air would be
500 / 1.55
= 323 Pa
Note that the operating pressure 500 Pa is used for selecting the fan.
The power consumption according the manufacturing data is 4 kW. According the chart the power coefficient is approximately 0.65. The correct power consumption should be
4 kW × 0.65
= 2.6 kW
Note! - the power consumption is lower in operating condition than during start up. A motor (and the motor protection) should in general be big enough to handle higher start up power consumption.
Remember! If a fan starts with temperatures below 20 oC (NTP) - the power consumption will be higher than specified in the catalogue - and the fan may be stopped by the electrical overload protection. The power consumption during start up can be reduced by limiting the volume flow with a closing damper on the outlet of the fan.