Vacuum
Vacuum is defined as air pressure below atmospheric pressure.
The vacuum level is the difference in pressure between atmospheric pressure and pressure in the evacuated system:
- 0% vacuum = 760 torr = 14.7 psia = 29.92 inc mercury abs = 101.4 kPa abs
- 50% vacuum = 380 torr = 7.3 psia = 15 inc mercury abs = 50.8 kPa abs
- 99.9% vacuum = 1 torr = 0.01934 psia = 0.03937 inc mercury abs = 1.3 kPa abs
For perfect vacuum (100%) - the pressure is 0 torr, 0 psia or 0 Pa abs.
Vacuum versus Absolute Air Pressure
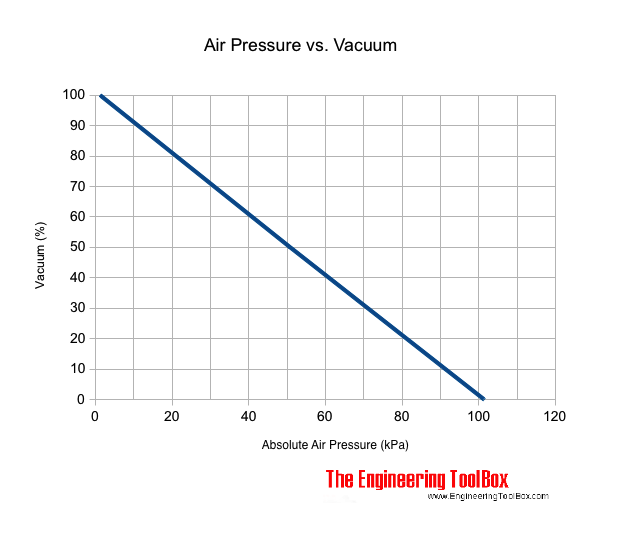
Example - Vacuum
If the absolute pressure is 60 kPa the vacuum according the diagram above is approximately 40 % - or approximately 450 Torr.
Vacuum Ranges
- atmospheric pressure - 760 torr
- low vacuum - 760 to 25 torr
- medium vacuum - 25 to 10-3 torr
- high vacuum - 10-3 to 10-9torr
- ultra high vacuum - 10-9to 10-12 torr
- extremely high vacuum - < 10-12 torr
- perfect vacuum - 0 torr <



