Propagation of Sound Indoors - the Room Constant
In a room the sound or noise will reach the receiver as direct and reverberant sound.
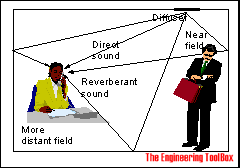
For a continuing sound source in a room the sound level is the sum of direct and reverberant sound. The sound pressure level for a receiver can be expressed as:
L p = L N + 10 log (D / (4 π r 2) + 4 / R) (1)
where
L p = received sound pressure level (dB)
L N = sound power level from source (dB)
D = directivity coefficient (typical 1 for receivers in the middle of the room)
R = room constant (m 2 Sabin)
π = 3.14 ....
r = distance from source (m)
Room Constant
The room constant express the acoustic property of a room.
R = A / (1- α m)
= Σ S i α i / (1- α m) (2)
where
R = room constant (m 2 Sabine)
A = total room sound absorption (m 2 Sabine)
α m = mean absorption coefficient of the room
S i = individual surface area in the room (m 2)
α i = absorption coefficient for individual surface in the room
Example - Received Sound
The sound power generated from a machine is 90 dB. The machine is located in a room with total sound aborption 12.2 m 2 Sabine and mean absorption coefficient 0.2.
The room constant can be calculated as
R = (12.2 m 2) / (1 - 0.2)
= 15.3 m 2 Sabine
For a receiver located in the middle of the room with a directivity coefficient 1 and distance 2 m from the source - the received sound pressure level can calculated as
L p = (90 dB) + 10 log (1 / (4 π (2 m) 2) + 4 / (15.3 m 2 Sabine ))
= 84.8 dB
Related Topics
-
Acoustics
Room acoustics and acoustic properties. decibel A, B and C calculations. Noise Rating (NR) curves. Sound transmission through walls. Calculate sound pressure, sound intensity and sound attenuation. -
Noise and Attenuation
Noise is usually defined as unwanted sound - noise, noise generation, silencers and attenuation in HVAC systems.
Related Documents
-
Maximum Sound Pressure Levels in Rooms
Maximum recommended sound pressure levels in rooms like kindergartens, auditoriums, libraries, cinemas and more. -
Noise from Machines - Enclosures and Sound Pressure Level Reductions
Barriers and enclosures to reduce noise sound pressure levels from machines. -
Sound - Attenuation and the Directivity Coefficient
The attenuation in a room depends on the location of the sound source and the receiver - and the room constant. -
Sound - Reverberation Time
The sound reverberation time indicates how long it takes until the sound pressure level in a room is decreased with 60 dB. -
Sound - Room Absorption Characteristics
Mean absorption coefficients and reverberation times in typical rooms. -
Sound - Room Absorption Coefficients
Room sound absorption and absorption coefficients for common materials like plaster walls, brickwork, plywood panels and more. -
Sound - Room Attenuation in Direct Sound Fields
Room size, absorption characteristics - and attenuation in direct sound fields. -
Sound Intensity
Acoustic power of sound per unit area. -
Sound Pressure
Sound Pressure is the force of sound on a surface perpendicular to the propagation of sound.




