Hooke's Law
Hooke's law - force, elongation and spring constant.
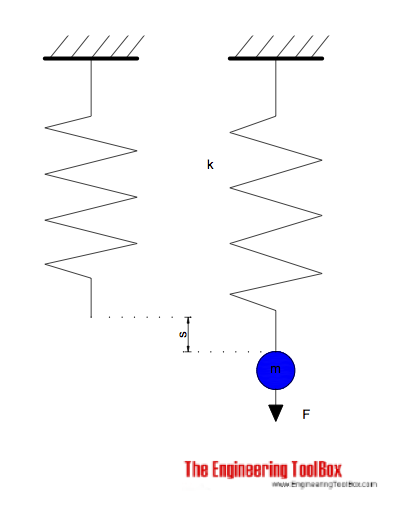
The force required to extend or compress a spring can be expressed with Hooke's Law as
F = - k s (1)
where
F = force (N)
k = spring constant (N/m)
s = extension or compression distance (m)
Example - Car Suspension
The maximum compression of a car suspension with mass 2000 kg (500 kg on each wheel) shall not exceed 0.1 m.
The force acting on each spring can be calculated using Newton's Second Law
F = (500 kg) (9.81 m/s2)
= 4905 N
= 4.9 kN
The required spring constant for the suspension can be calculated with (1) as
k = - F / s
= - (4905 N) / (- 0.1 m)
= 49050 N/m
= 49 kN/m
Note that this is the value for the static load of the car. You may probably at least double the value for handling dynamic forces, potholes and similar.
Hook's Law of Elasticity
In the generalized variation of Hooke's law it states that the strain/deformation of an elastic object or material is proportional to the stress applied to it. It may be expressed mathematically as
σ = E ε (2)
where
σ = stress (Pa)
E = Young's Modulus of Elasticity (Pa)
ε = strain (m/m)



