Convective Air Flow - Single Heat Source
Calculate the vertical air flow and air velocity generated by a single heat source.
A heat source, like an engine, stove, melting pot or a person, will generate a convective vertical air flow as indicated in the figure below.
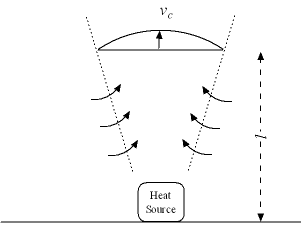
Air Velocity
The air velocity in the center of the air flow at a distance above the floor can be calculated as
vc = c1 (P / l)1/3 (1)
where
vc = air velocity in center of the air flow (m/s)
c1 = constant characterizing the actual application, typical values ranging 1 to 2
P = heat power from the source (kW)
l = distance above the floor and the heat source (m)
Air Flow Volume
The air flow volume in a distance above the the floor can be calculated as
Q = c2 P1/3 l5/3 (2)
where
Q = air flow volume (m3/s)
c2 = constant characterizing the actual application, values ranging 0.05 to 0.15 (typical 0.06)
Example - Convective Air Flow above an Engine
The heat loss from the surface of an engine is 10 kW. If c1 = 1.5, the air velocity 3 meters above the engine can be estimated to
vc = 1.5 ((10 kW) / (3 m))1/3
= 2.2 m/s
With c2 = 0.06 the volume flow can be estimated to
Q = 0.06 (10 kW)1/3 (3 m)5/3
= 0.8 m3/s
Related Topics
-
Heating Systems
Design of heating systems - capacities and design of boilers, pipelines, heat exchangers, expansion systems and more.
Related Documents
-
Convective Air Flow from Heat Source
Convective air flows from typical heat sources like people, computers, radiators and more. -
Convective Heat Transfer
Heat transfer between a solid and a moving fluid is called convection. This is a short tutorial about convective heat transfer. -
Convective Heat Transmission - Air Velocity and Air Flow Volume
Hot or cold vertical surfaces generates vertical air flows - calculate air velocity and volume flow. -
Exhaust Hoods
Sizing of exhaust hoods - air volume flow and capture velocities - online exhaust hood calculator.




