Convective Heat Transmission - Air Velocity and Air Flow Volume
Hot or cold vertical surfaces generates vertical air flows - calculate air velocity and volume flow.
A hot or cold vertical surface will generate a vertical upwards or downwards air flow as indicated in the figure below.
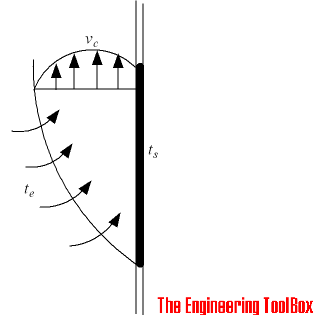
The air velocity in the center of a convective air flow in parallel to the hot or cold surface - at a vertical distance - can be estimated as:
Air Velocity
vc = 0.65 [g l dt / (273 + te)]1/2 (1)
where
vc = velocity in center of airflow (m/s)
g = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/s2)
l = vertical distance from bottom (or top) of the surface (m)
dt = te - ts= temperature difference between surface and room environment
ts = surface temperature (oC)
te = surrounding environment - ambient - temperature (oC)
For a cold surface where the air will flow downwards - the value will be negative.
Air Volume
Convective air flow volume at a vertical distance generated by the hot or cold surface can be calculated as
Q = 0.019 [g (te - ts) / (273 + te)]0.4 l1.2 (2)
where
Q = air flow volume (m3/s per meter surface width)
Example - Convective Air Flow from a Cold Window
The air velocity at the lower level of a cold (5oC) window with height 2 m in a room with temperature 20oC can be calculated as
vc = 0.65 [(9.81 m/s2) (2 m) ((20 oC) - (5 oC)) / (273 + (20 oC))]1/2
= 0.65 m/s
The air flow volume (for a window with width 1m) can be calculated as
Q = 0.019 [(9.81 m/s2) ((20 oC) - (5 oC) / (273 + (20 oC))]0.4 (2 m)1.2
= 0.033 m3/s
= 119 m3/h
Example - A Heating Element (or Radiator) and Convective Air Flow
The air flow velocity at the top of a hot (80oC) radiator with height 1 m in a room with temperature 20oC can be calculated as
vc = 0.65 [(9.81 m/s2) (1 m) ((80 oC) - (20 oC) / ((273 K) + (20 oC))]1/2
= 0.92 m/s
The air flow volume (for radiator with width 1 m) can be calculated as
Q = 0.019 [(9.81 m/s2) ((80 oC) - (20 oC) / ((273 K) + (20 oC))]0.4 (1 m)1.2
= 0.025 m3/s
= 90.4 m3/h
Related Topics
-
Heating Systems
Design of heating systems - capacities and design of boilers, pipelines, heat exchangers, expansion systems and more.
Related Documents
-
Convective Air Flow - Single Heat Source
Calculate the vertical air flow and air velocity generated by a single heat source. -
Convective Air Flow from Heat Source
Convective air flows from typical heat sources like people, computers, radiators and more. -
Convective Heat Transfer
Heat transfer between a solid and a moving fluid is called convection. This is a short tutorial about convective heat transfer. -
Steam Radiators and Convectors - Heating Capacities
Steam radiators and steam convectors - heating capacities and temperature coefficients.




