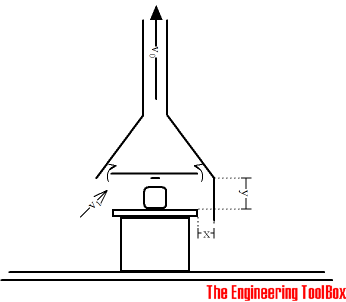
Exhaust Hoods
Sizing of exhaust hoods - air volume flow and capture velocities - online exhaust hood calculator.
Exhaust hoods are essential in kitchens, laboratories and industrial application for removing
- fumes
- mists
- vapors
- aerosols
- particulates
- hazardous substances
- polluting contaminants
before they "escapes" to from the surrounding air.
In general for an exhaust hood to be efficient
- the height - y - should not exceed 1.20 m (4 ft)
- the distance - x - should not be less than 1/3 y
- the capture velocity - v1 - should not be less than 0.15 - 0.20 m/s (30 - 40 ft/min)
Note! Potential hazardous and polluting applications requires special solutions. Always check local regulations before design.
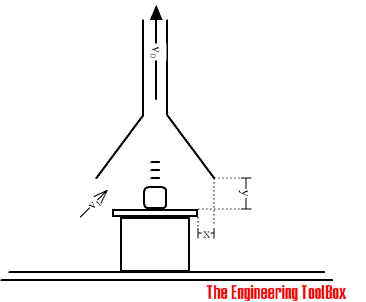
Capture velocity - v1 - for an exhaust hood can be estimated with the empirical equation
v1 = q / 2 y2 c (1)
where
v1 = capturing velocity (m/s)
q = air volume flow (m3/s)
y = distance between table and exhaust hood (m)
c = circumference of the hood (m)
(1) can be modified to calculate air volume flow
q = 2 v1 y2 c (1a)
Example - Kitchen Exhaust Hood
Required air volume flow for a exhaust hood with circumference 3 m located 1.2 m above a stove can be calculated as
q = 2 (0.2 m/s) (1.2 m2)2 (3 m)
= 1.7 m3/s
Note! The units don't match since the equation is empirical (a result of experiments).
Exhaust Hood Calculator
The air flow volume in the exhaust hood can be calculated below
Exhaust Hood with internal Plate
The efficiency of an exhaust hood can be improved by adding an internal plate.
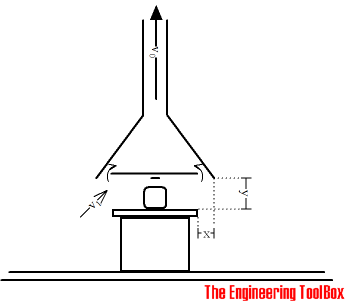
The required air volume for an exhaust hood with an internal plate can in general be reduced to approximately 80% compared to an exhaust hood without a plate.
Exhaust Hood with Side Walls
The exhaust hood efficiency can be further improved by adding side walls.