12 Volt - Maximum Wire Length vs. Current
Maximum length of copper wire with 2% voltage drop.
Maximum Wire Length Calculator
The calculator can be used to calculate maximum length of copper wires. Note that
- for a typical electrical circuit with two wires - one back and one forth - this is the length of the two wires together. The maximum distance between the source and the equipment is half the calculated distance
- in a car where equipment can be grounded to the chassis - the body of the car acts as the negative wire. The electrical resistance in the chassis can normally be neglected and the maximum distance equals the calculated distance
Maximum lengths for copper conductors from power source to loads in 12 volt systems with 2% voltage drop are indicated below:
Wire Length - feet
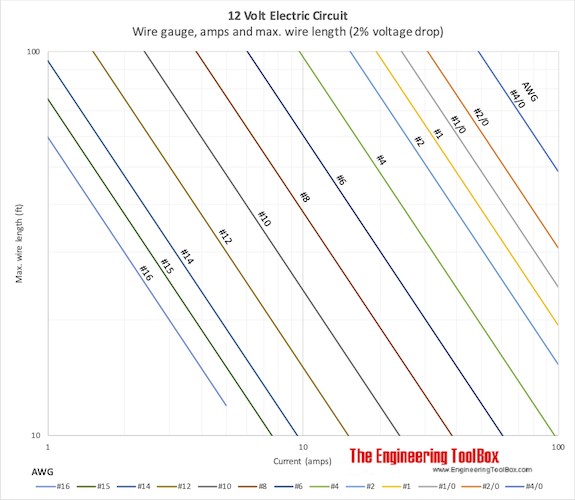
Download and print 12 Volt Electric Circuit Chart
Wire Length - meter
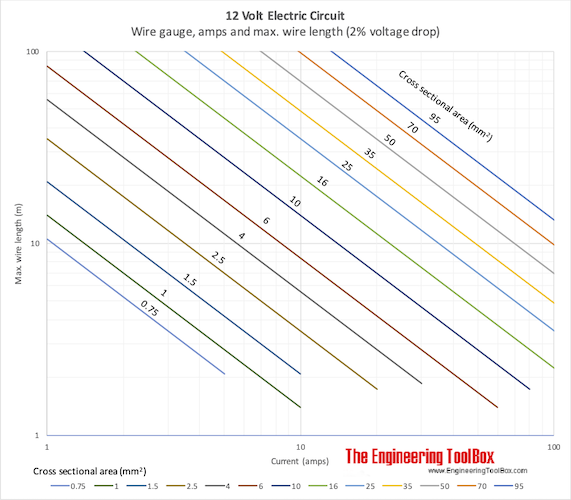
Download and print 12 Volt Electric Circuit Chart
- double the distance if 4% loss is acceptable
- multiply distance by 2 for 24 volts
- multiply distance by 4 for 48 volts
Example - Maximum Length of Wire
The current to a light bulb with power 50 W can be calculated with Ohm's law
I = P / U (1)
where
I = current (amps)
P = power (watts)
U = voltage (volts)
(1) with values
I = (50 W) / (12 V)
= 4.2 A
From the diagram above the maximum length of the total wire back and forth should not exceed approximately 8 m for gauge #10 (5.26 mm2) . By increasing the size of the wire to gauge #2 (33.6 mm2) the maximum length is limited to approximately 32 m .
Example - Calculate Maximum Wire Length
The electrical resistance in a copper conductor with cross sectional area 6 mm2 is 2.9×10-3 ohm/m . This is close to wire gauge 9.
In a 12V system with maximum 2% voltage drop - and current 10 amps - the maximum total length of the wire back and forth can be calculated with Ohm's law
U = R L I (2)
where
R = electrical resistance (ohm/m)
L = length of wire (m)
(2) rearranged for L
L = U / (R I) (2b)
(2b) with values
L = (12 V) 0.02 / (( 2.9×10-3 ohm/m) (10 amps))
= 8.3 m



