Pneumatic Powder and Solid Transport Systems
Pneumatic transport systems used to move powder and other solid products.
Some common solids as flour, sugar, cement and many more, can be suspended and transported in air - referred to as pneumatic conveying. A pneumatic conveying system may transport solids up to approximately 50 mm in size. The powder or solid must be dry with no more than 20% moisture and not sticking.
In a pneumatic conveying system most of the energy is used for transport of the air itself. The energy efficiency of a pneumatic conveying plant is therefore relatively low, but this is often outweighed by easy handling and, in well designed systems, dust free solutions.
In general - the length of a pneumatic system should not extend 300 m for each pneumatic unit. Products can be conveyed over long distances by connecting systems in series.
There are three basic designs of pneumatic transport systems:
- dilute phase conveying at high air velocity (20 - 30 m/s)
- strand conveying at limited air velocity (15 - 20 m/s)
- dense phase conveying at low air velocity (5 - 10 m/s)
Pneumatic systems can operate with both positive and negative pressure (vacuum). The working pressure should not extend 40 kN/m2.
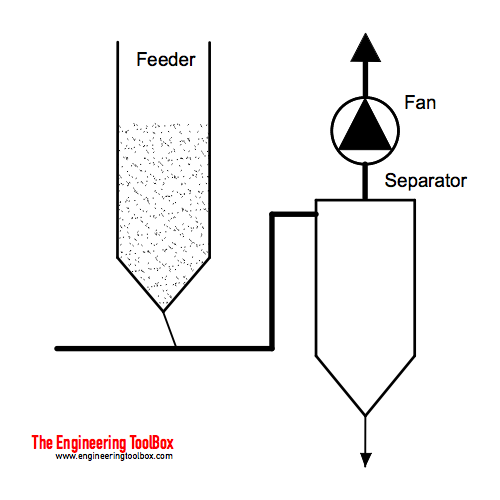
Negative Pressure Pneumatic Conveying System
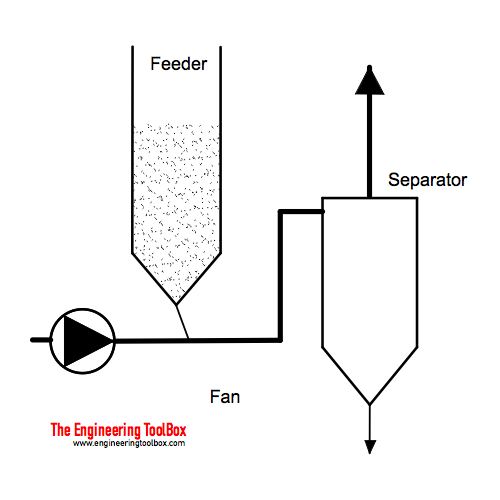
Positive Pressure Pneumatic Conveying System
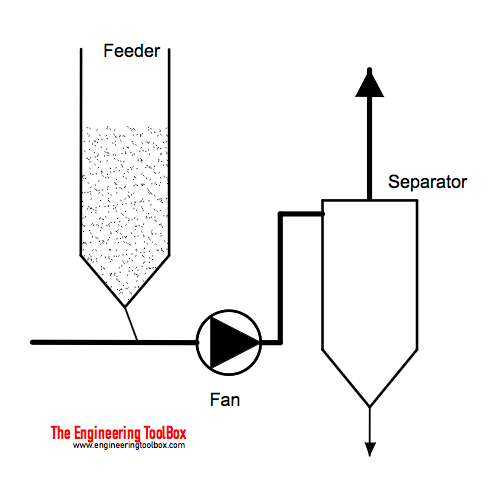
Combination Pressure Pneumatic Conveying System
Maximum temperature rise during the pneumatic compression is seldom more than 5 oC which makes pneumatic transport systems suitable to sensitive products like medicines, food and similar.