Laminar Flow - Friction Coefficients
Calculate friction coefficients for laminar fluid flow.
The friction coefficient - or factor - of a fluid flow at laminar conditions can be calculated as
λ = 64 / Re
= 64 μ / (dh u ρ)
= 64 ν / (dh u) (1)
where
λ = friction coefficient (non-dimensional)
Re = Reynolds Number (non-dimensional)
μ = absolute (dynamic) viscosity (Ns/m2, lbm/s ft)
dh = hydraulic diameter (mm, ft)
u = mean velocity in flow (m/s, ft/s)
ρ = density of fluid (kg/m3, lbm/ft3)
ν = μ / ρ = kinematic viscosity (m2/s, ft2/s)
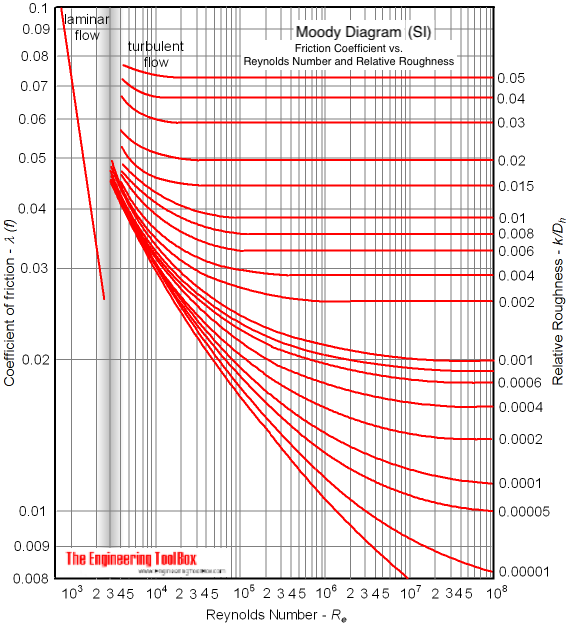
Equation (1) is only valid at laminar conditions where Reynolds Number is less than 2300. For turbulent conditions where Reynolds Number exceeds 4000 the Colebrook equation should be used to calculate the friction coefficient.
In practice laminar flow is only actual for viscous fluids - like crude oil, fuel oil and other oils.
The friction coefficient for laminar flow indicated in the Moody diagram (SI based):