Industrial Lubricants - Viscosities vs. ISO-VG Grade
ISO-VG viscosity grades for industrial lubricants.
The diagram below indicates the minimum and maximum viscosities in centistokes for equivalent ISO-VG grades at temperature 40 oC.
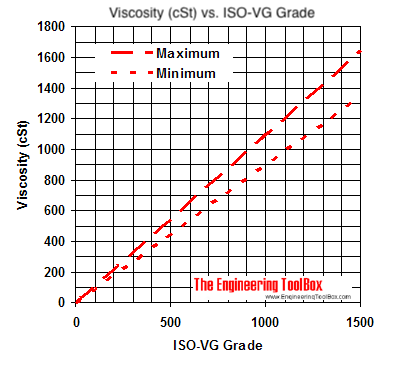
ISO VG stands for "International Standards Organization Viscosity Grade" and is a number ranged from 2 to 1500.
Equivalent Viscosities of ISO-VG Grades at 40 oC and SAE Crankcase Oil Grades
| ISO-VG Grade | SAE Crankcase Oil Grade |
|---|---|
| 22 | 5W |
| 32 | 10W |
| 46 | 15W |
| 68 | 20W |
| 100 | 30 |
| 150 | 40 |
| 220 | 50 |
| 320 | 60 |
Equivalent Viscosities of ISO-VG Grades at 40 oC and SAE Aircraft Oil Grades
| ISO-VG Grade | SAE Aircraft Oil Grade |
|---|---|
| 100 | 65 |
| 150 | 80 |
| 220 | 100 |
| 320 | 120 |
Equivalent Viscosity of ISO-VG Grades at 40 oC and SAE Gear Lube Grades
| ISO-VG Grade | SAE Gear Lube Grade |
|---|---|
| 46 | 75W |
| 100 | 80W-90 |
| 220 | 90 |
| 460 | 85W-140 |
| 1500 | 250 |
Equivalent Viscosity of ISO-VG Grades at 40 oC and AGMA Gear Lube Grades
| ISO-VG Grade | AGMA Gear Lube Grade | |
|---|---|---|
| Regular | EP | |
| 46 | 1 | |
| 68 | 2 | 2 EP |
| 100 | 3 | 3 EP |
| 150 | 4 | 4 EP |
| 220 | 5 | 5 EP |
| 320 | 6 | 6 EP |
| 460 | 7 | 7 EP |
| 680 | 8 | 8 EP |
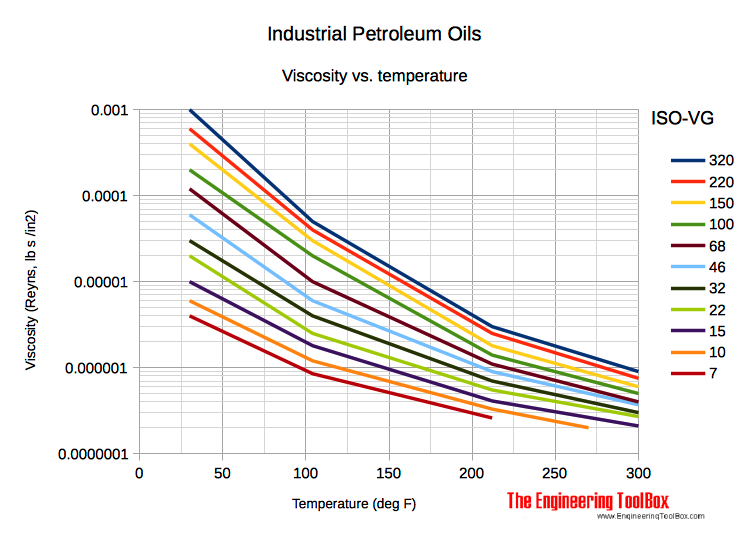
ISO-VG Grades - Absolute Viscosity vs. Temperature, Reyns vs. Fahrenheit
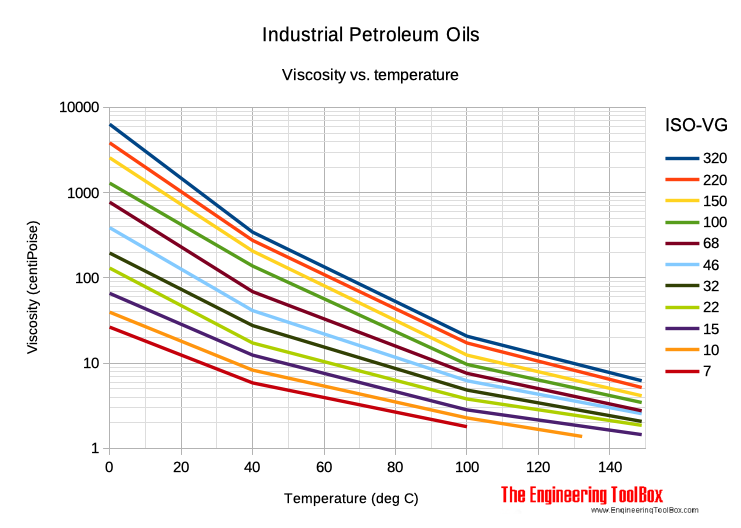
ISO-VG Grades - Absolute Viscosity vs. Temperature, centiPoise vs. Celsius
- tC = 5/9 (tF - 32)
- tF = 9/5 tC + 32
- 1 reyns (lb s/in2) = 6896.55 (Pa s)
- 1 cSt (centiStoke) = 1 centiPoise / SG
- SG = specific gravity of oil



