Galvanic Corrosion vs. Electrode Potential
Introduction to electro chemical series and corrosion of metals.
The potential difference between an anode and a cathode can be measured by a voltage measuring device but since the absolute potential of an anode or cathode cannot be measured directly - all potential measurements are made against a standard electrode. The standard electrode potential is set to zero and the measured potential difference can be considered as absolute.
Standard Hydrogen Electrode
- The half-cell in which the hydrogen reaction takes place is called the Standard Hydrogen Electrode - SHE
Standard Electrode Potential
- The potential difference measured between a metal M and the Standard Hydrogen Electrode - SHE
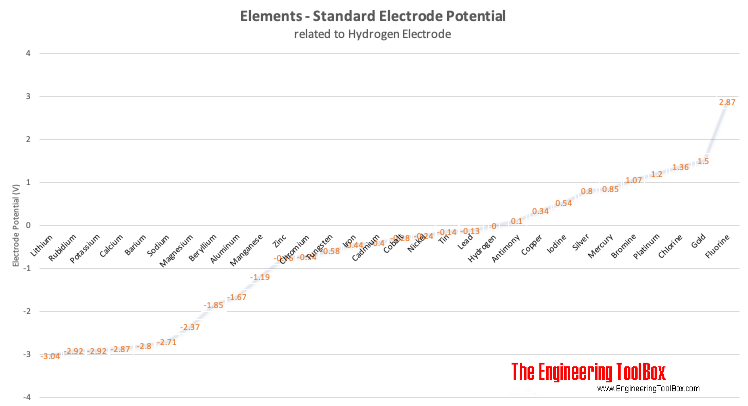
The electro-chemical series (electro-motive series) is a list of metals arranged in order of their standard potentials to the hydrogen electrode:
| Element | Electrode Potential (volts) |
|---|---|
| Lithium | -3.04 |
| Rubidium | -2.92 |
| Potassium | -2.92 |
| Calcium | -2.87 |
| Barium | -2.80 |
| Sodium | -2.71 |
| Magnesium | -2.37 |
| Beryllium | -1.85 |
| Aluminum | -1.67 |
| Manganese | -1.19 |
| Zinc | -0.76 |
| Chromium | -0.74 |
| Tungsten | -0.58 |
| Iron | -0.44 |
| Cadmium | -0.40 |
| Cobalt | -0.28 |
| Nickel | -0.24 |
| Tin | -0.14 |
| Lead | -0.13 |
| Hydrogen | +0.00 |
| Antimony | +0.10 |
| Copper | +0.34 |
| Iodine | +0.54 |
| Silver | +0.80 |
| Mercury | +0.85 |
| Bromine | +1.07 |
| Platinum | +1.20 |
| Chlorine | +1.36 |
| Gold | +1.50 |
| Fluorine | +2.87 |
Note! - metals higher up in the electro-chemical series displaces metals lower in the series - which means that when connecting two metals with different potentials the metal with the lowest potential corrodes.
Corrosion Problem when Connecting Copper and Iron/Steel
A very common connection in piping systems are copper and iron/steel. with this connection iron/steel corrodes many times faster than iron/steel alone.
Related Topics
-
Corrosion
Corrosion in piping systems caused by thermodynamic and electrochemical processes - corrosion problems and methods of protection and prevention. -
Electrical
Electrical engineering with units, amps and electrical wiring. Wire gauges, electrical formulas, motors and more. -
Miscellaneous
Engineering related topics like Beaufort Wind Scale, CE-marking, drawing standards and more.
Related Documents
-
Copper Tubes - Corrosion Resistance to Chemicals
Copper tubes corrosion resistance to different products and chemicals. -
Elements - Boiling Points
Elements and their boiling points. -
Feed Water Treatment to Avoid Corrosion
Make-up water to steam boilers should be treated with oxygen scavengers to avoid serious corrosion problems. -
Metals - Corrosion Resistance to Aggresive Fluids
Common metals and their corrosion resistance to aggressive fluids like acids, bases and more. -
Metals - Specific Heats
Specific heat of commonly used metals like aluminum, iron, mercury and many more - imperial and SI units. -
Metals in Seawater - Galvanic Series
Galvanic series of metals in seawater. -
Metals, Metallic Elements and Alloys - Thermal Conductivities
Thermal conductivities of common metals, metallic elements aand alloys. -
Pipes - Corrosion Protection
A corrosion protection tutorial for piping systems. -
Piping Materials - Galvanic Corrosion
Connecting pipes of different materials may cause galvanic corrosion and serious damage. -
Potassium - Thermophysical Properties vs. Temperature
Thermophysical properties of potassium. -
Silver Binary Eutectic Alloys - Melting Points
Ag - Silver - binary eutectic alloys and melting points. -
Stainless Steels - Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistanse of AISI stainless steels in various environments. -
Steel Pipes - Corrosion due to Oxygen
The influence of oxygen concentration and temperature on the corrosion of steel pipes. -
Types of Corrosion
Uniform, pitting, galvanic, crevice, concentration cell and graphitic types of corrosion.




