Arithmetic and Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference
Arithmetic Mean Temperature Difference in Heat Exchangers - AMTD - and Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference - LMTD - formulas with examples - Online Mean Temperature Calculator.
According to Newton's Law of Cooling heat transfer rate is related to the instantaneous temperature difference between hot and cold media
- in a heat transfer process the temperature difference vary with position and time
Mean Temperature Difference
The mean temperature difference in a heat transfer process depends on the direction of fluid flows involved in the process. The primary and secondary fluid in an heat exchanger process may
- flow in the same direction - parallel flow or co-current flow
- in the opposite direction - counter-current flow
- or perpendicular to each other - cross flow
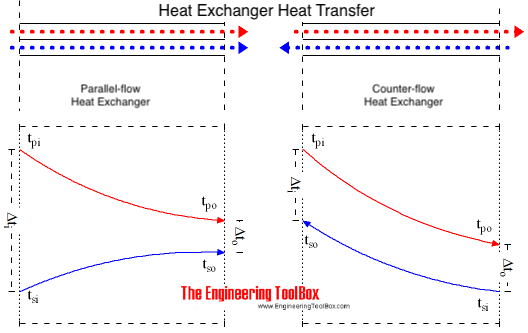
With saturation steam as the primary fluid the primary temperature can be taken as a constant since the heat is transferred as a result of a change of phase only. The temperature profile in the primary fluid is not dependent on the direction of flow.
Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference - LMTD
The rise in secondary temperature is non-linear and can best be represented by a logarithmic calculation. A logarithmic mean temperature difference is termed
- LMTD (or DTLM) - Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference
LMTD can be expressed as
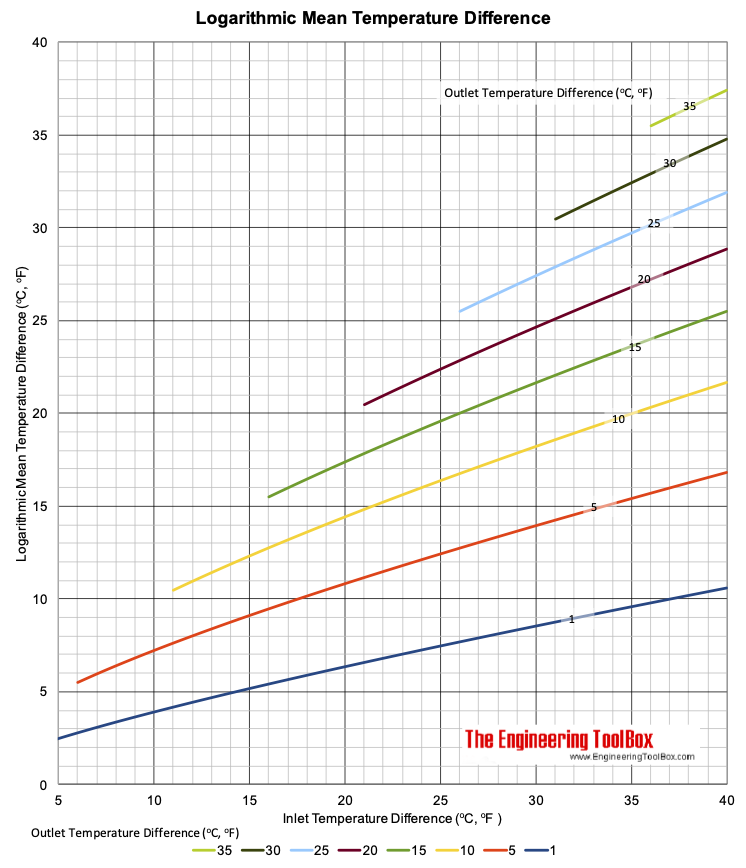
LMTD = (dto - dti) / ln(dto / dti) (1)
where
LMTD = Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference (oF, oC)
For parallel flow:
dti = tpi - tsi = inlet primary and secondary fluid temperature difference (oF, oC)
dto = tpo - tso = outlet primary and secondary fluid temperature difference (oF, oC)
For counter flow:
dti = tpi - tso = inlet primary and outlet secondary fluid temperature difference (oF, oC)
dto = tpo - tsi = outlet primary and inlet secondary fluid temperature difference (oF, oC)
The Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference is always less than the Arithmetic Mean Temperature Difference.
Arithmetic Mean Temperature Difference - AMTD
An easier but less accurate way to calculate the mean temperature difference is the
- AMTD (or DTAM) - Arithmetic Mean Temperature Difference
AMTD can be expressed as:
AMTD = (tpi + tpo) / 2 - (tsi + tso) / 2 (2)
where
AMTD = Arithmetic Mean Temperature Difference (oF, oC)
tpi = primary inlet temperature (oF, oC)
tpo = primary outlet temperature (oF, oC)
tsi = secondary inlet temperature (oF, oC)
tso = secondary outlet temperature (oF, oC)
A linear increase in the secondary fluid temperature makes it more easy to do manual calculations. AMTD will in general give a satisfactory approximation for the mean temperature difference when the smallest of the inlet or outlet temperature differences is more than half the greatest of the inlet or outlet temperature differences.
When heat is transferred as a result of a change of phase like condensation or evaporation the temperature of the primary or secondary fluid remains constant. The equations can then be simplified by setting
tp1 = tp2
or
ts1 = ts2
Arithmetic and Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference Calculator
The calculator below can be used to calculate Arithmetic and Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference of counter-flow an parallel-flow heat exchangers.
Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference Chart
Example - Arithmetic and Logarithmic Mean Temperature, Hot Water Heating Air
Hot water at 80 oC heats air from from a temperature of 0 oC to 20 oC in a parallel flow heat exchanger. The water leaves the heat exchanger at 60 oC.
Arithmetic Mean Temperature Difference can be calculated as
AMTD = ((80 oC) + (60 oC)) / 2 - ((0 oC) + (20 oC)) / 2
= 60 oC
Logarithmic Mean Temperature Difference can be calculated as
LMTD = ((60 oC) - (20 oC)) - ((80 oC) - (0 oC))) / ln(((60 oC) - (20 oC)) / ((80 oC) - (0 oC)))
= 57.7 oC
Example - Arithmetic and Logarithmic Mean Temperature, Steam Heating Water
Steam at 2 bar gauge heats water from 20 oC to 50 oC. The saturation temperature of steam at 2 bar gauge is 134 oC.
Note! that steam condenses at a constant temperature. The temperature on the heat exchangers surface on the steam side is constant and determined by the steam pressure.
Arithmetic Mean Temperature Difference can be calculated like
AMTD = ((134 oC) + (134 oC)) / 2 - ((20 oC) + (50 oC)) / 2
= 99 oC
Log Mean Temperature Difference can be calculated like
LMTD = ((134 oC) - (20 oC) - ((134 oC) - (50 oC))) / ln(((134 oC) - (20 oC)) / ((134 oC) - (50 oC)))
= 98.24 oC
Related Topics
-
Heat Loss and Insulation
Heat loss from pipes, tubes and tanks - with and without insulation. Use of materials lke foam, fiberglass, rockwool and more. -
Insulation
Calculate heat transfer and heat loss from buildings and technical applications. Heat transfer coefficients and insulation methods available for reduction of energy consumption. -
Thermodynamics
Calculate heat, work, temperature and energy. The thermodynamics of steam and condensate systems. Water and Ice properties. -
Thermodynamics
Work, heat and energy systems.
Related Documents
-
Condensation of Steam - Heat Transfer
Heat transfer when steam condensates. -
Conductive Heat Transfer
Conductive heat transfer takes place in a solid if there is a temperature gradient. -
Convective Heat Transfer
Heat transfer between a solid and a moving fluid is called convection. This is a short tutorial about convective heat transfer. -
Cooling and Heating Equations
Latent and sensible cooling and heating equations - imperial units. -
Copper Tubes - Uninsulated Heat Losses
Heat loss from uninsulated copper pipes - dimensions ranging 1/2 - 4 inches. -
Heat Emission from Radiators and Heating Panels
The heat emission from a radiator or a heating panel depends on the temperature difference between the radiator and the surrounding air. -
Heat Exchangers - Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients
Overall heat transfer coefficients in common heat exchanger designs - tubular, plate or spiral. -
Heat Transfer Coefficients in Heat Exchanger Surface Combinations
Average overall heat transmission coefficients for fluid and surface combinations like Water to Air, Water to Water, Air to Air, Steam to Water and more. -
Heaters and Coolers in Ventilation Systems
Basic equations for heat transfer - selecting criteria for heaters and coolers in ventilations systems. -
Logarithms
The rules of logarithms - log10 and loge for numbers ranging 1 to 1000. -
Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients
Walls or heat exchangers - calculate overall heat transfer coefficients. -
Properties of Saturated Steam - SI Units
Saturated Steam Table with steam properties as specific volume, density, specific enthalpy and specific entropy. -
Steam & Condensate Equations
Steam consumption and condensate generation when heating liquid or gas flows -
Steam Radiators and Convectors - Heating Capacities
Steam radiators and steam convectors - heating capacities and temperature coefficients. -
Submerged Coils - Heat Transfer Coefficients
Heat transfer coefficients for steam and hot water coils submerged in oil tanks. -
Temperature
Introduction to temperature - including Celsius, Fahrenheit, Kelvin and Rankine definitions - and an online temperature converter. -
Transmission Heat Loss through Building Elements
Heat loss through common building elements due to transmission, R-values and U-values - imperial and SI units. -
WABT - Weighted Average Bed Temperature
Definition and examples of calculation of weighted average bed temperature in adiabatic reactors.