Understanding Convective Heat Transfer: Coefficients, Formulas & Examples
Heat transfer between a solid and a moving fluid is called convection. This is a short tutorial about convective heat transfer.
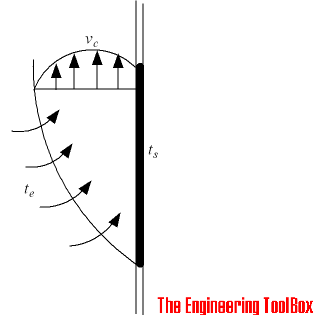
Heat energy transferred between a surface and a moving fluid with different temperatures - is known as convection.
In reality this is a combination of diffusion and bulk motion of molecules. Near the surface the fluid velocity is low, and diffusion dominates. At distance from the surface, bulk motion increases the influence and dominates.
Convective heat transfer can be
- forced or assisted convection
- natural or free convection
Forced or Assisted Convection
Forced convection occurs when a fluid flow is induced by an external force, such as a pump, fan or a mixer.
Natural or Free Convection
Natural convection is caused by buoyancy forces due to dens ity differences caused by temperature variations in the fluid. At heating the density change in the boundary layer will cause the fluid to rise and be replaced by cooler fluid that also will heat and rise. This continues phenomena is called free or natural convection.
Boiling or condensing processes are also referred to as a convective heat transfer processes.
- The heat transfer per unit surface through convection was first described by Newton and the relation is known as the Newton's Law of Cooling.
The equation for convection can be expressed as:
q = hc A dT (1)
where
q = heat transferred per unit time (W, Btu/hr)
A = heat transfer area of the surface (m2, ft2)
hc = convective heat transfer coefficient of the process (W/(m2oC, Btu/(ft2 h oF))
dT = temperature difference between the surface and the bulk fluid (oC, F)
Heat Transfer Coefficients - Units
- 1 W/(m2K) = 0.85984 kcal/(h m2 oC) = 0.1761 Btu/(ft2 h oF)
- 1 Btu/(ft2 h oF) = 5.678 W/(m2 K) = 4.882 kcal/(h m2 oC)
- 1 kcal/(h m2 oC) = 1.163 W/(m2K) = 0.205 Btu/(ft2 h oF)
Convective Heat Transfer Coefficients
Convective heat transfer coefficients - hc - depends on type of media, if its gas or liquid, and flow properties such as velocity, viscosity and other flow and temperature dependent properties.
Typical convective heat transfer coefficients for some common fluid flow applications:
- Free Convection - air, gases and dry vapors : 0.5 - 1000 (W/(m2K))
- Free Convection - water and liquids: 50 - 3000 (W/(m2K))
- Forced Convection - air, gases and dry vapors: 10 - 1000 (W/(m2K))
- Forced Convection - water and liquids: 50 - 10000 (W/(m2K))
- Forced Convection - liquid metals: 5000 - 40000 (W/(m2K))
- Boiling Water : 3.000 - 100.000 (W/(m2K))
- Condensing Water Vapor: 5.000 - 100.000 (W/(m2K))
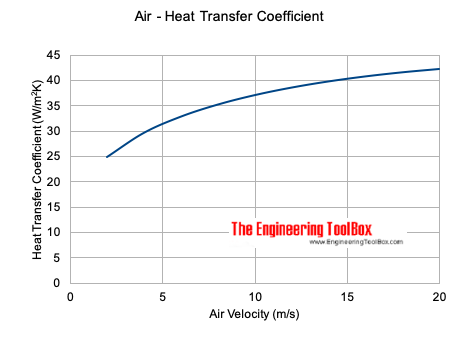
Convective Heat Transfer Coefficient for Air
The convective heat transfer coefficient for air flow can be approximated to
hc = 10.45 - v + 10 v1/2 (2)
where
hc = heat transfer coefficient (kCal/m2h°C)
v = relative speed between object surface and air (m/s)
Since
1 kcal/m2h°C = 1.16 W/m2°C
or
1 W/m2°C = 0.862 kcal/m2h°C
(2) can be modified to
hcW = 1.16 (10.45 - v + 10 v1/2) (2b)
where
hcW = heat transfer coefficient (W/m2°C)
Note! - this is an empirical equation and can be used for velocities 2 to 20 m/s.
Example - Convective Heat Transfer
A fluid flows over a plane surface 1 m by 1 m. The surface temperature is 50oC, the fluid temperature is 20oC and the convective heat transfer coefficient is 2000 W/m2oC. The convective heat transfer between the hotter surface and the colder air can be calculated as
q = (2000 W/m2oC) ((1 m) (1 m)) ((50 oC) - (20 oC))
= 60000 (W)
= 60 (kW)