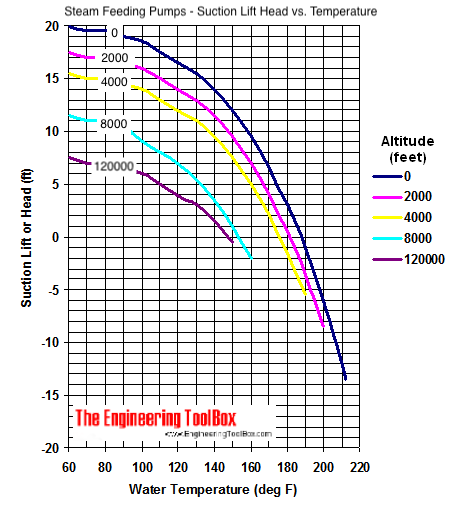
Feed Pumps in Steam Systems - Suction Lift Head vs. Temperature
Cavitation of impellers increases with water temperatures.
To avoid cavitation in a feed pump the suction lift and pressure head should not exceed the limits indicated below:
| Temperature of Feeding Water | Max Suction Lift | Minimum Pressure Head | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (oC) | (oF) | (m) | (ft) | (m) | (ft) |
| 55 | 130 | 3 | 10 | ||
| 65 | 150 | 2 | 7 | ||
| 77 | 170 | 0.6 | 2 | ||
| 80 | 175 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 87 | 190 | 1.5 | 5 | ||
| 95 | 200 | 3.5 | 10 | ||
| 99 | 210 | 4.5 | 15 | ||
| 100 | 212 | 5 | 17 | ||
For water with temperature above 80 oC (175 oF) it is necessary with a positive pressure head - and the pump is located in an elevation below the water or condensate receiver.
In steam distribution systems its common with open vented condensate receivers with temperatures close to 100 oC (212 oF). This is true especially in systems where most of the steam consumed is returned as hot condensate, but also in systems where the make up water is heated to reduce the amount of air dissolved in the water.
- Recommended Suction Flow Velocity for Boiling Fluids - Recommended flow velocity for the pump suction side.
- Recommended Delivery Flow Velocity for Boiling Liquids - Flow velocity normally required on the delivery side of the pump in systems with boiling liquids.
- 1 ft (foot) = 0.3048 m



