Piping Equations
Calculate cross-sectional areas, weight of empty pipes, weight of pipes filled with water, inside and outside surface areas.
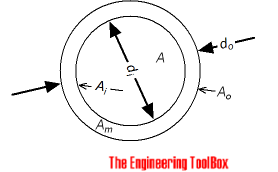
Cross Sectional inside Pipe Area
Cross-sectional inside area of a pipe can be calculated as
Ai = π (di / 2)2
= π di 2/ 4 (1)
where
Ai = cross-sectional inside area of pipe (m2, in2)
di = inside diameter (m, in)
Cross Sectional Pipe Wall Area
The cross-sectional wall area - or area of piping material - can be calculated as
Am = π (do / 2)2 - π (di / 2)2
= π (do 2 - di 2) / 4 (2)
where
Am = cross-sectional wall area of pipe (m2, in2)
do = outside diameter (m, in)
Weight of Empty Pipes
Weight of empty pipes per unit length can be calculated as
wp = ρm Am
= ρm (π (do / 2)2 - π (di / 2)2)
= ρm π (do2 - di2) / 4 (3)
where
wp = weight of empty pipe per unit length (kg/m, lb/in)
ρs = density of pipe material (kg/m3, lb/in3)
Weight of Liquid in Pipes
Weight of liquid in pipes per unit length can be calculated as
wl = ρl A
= ρl π (di / 2)2
= ρl π di2 / 4 (4)
where
wl = weight of liquid in pipe per unit length of pipe (kg, lb)
ρl = density of liquid (kg/m3, lb/in3)
Weight of Pipe filled with Liquid
Weight of pipe filled with liquid per unit length can be calculated as
w = wl + wp (5)
where
w = weight of pipe and liquid per unit length of pipe (kg, lb)
Outside Surface Area of Pipes
Outside surface area of steel pipes per unit length can be calculated as
Ao = 2 π (do / 2)
= π do (6)
where
Ao = outside area of pipe - per unit length of pipe (m2, in2)
Inside Surface Area of Pipes
Inside surface area of steel pipes per unit length can be calculated as
Ai = 2 π (di / 2)
= π di (7)
where
Ai = inside area of pipe - per unit length of pipe (m2, in2)



