Hydraulic Oil Pump - Horsepower vs. Pressure and Volume Flow
The power required for hydraulic pumping.
Horsepower required by a hydraulic pump can be calculated as
PHP = q p / 1714 (1)
where
PHP = horsepower (HP)
q = flow (gpm)
p = required pressure (psi)
- 1 gpm (US) =6.30888×10-5m3/s = 0.227 m3/h = 0.06309 dm3 (litre)/s = 2.228×10-3 ft3/s = 0.1337 ft3/min = 0.8327 gpm (UK)
- 1 psi (lb/in2) = 144 psf (lbf/ft2) = 6,894.8 Pa (N/m2) = 6.895×10-3 N/mm2 = 6.895×10-2 bar
- 1 hp = 745.7 W
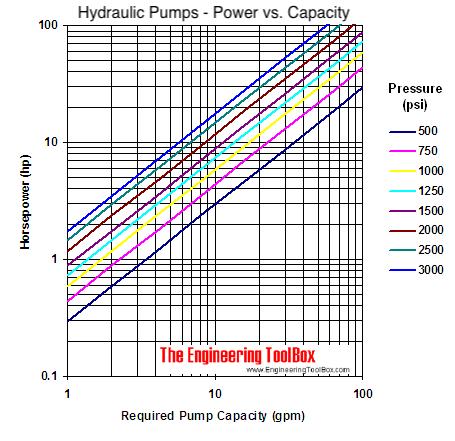
Example - Hydraulic Pump
The horsepower required by a a pump with flow 20 gpm and 1500 psi increase in pressure can be calculated as
PHP = (20 gpm) (1500 psi) / 1714
= 17.5 HP
Efficiency
Note that the equation above is for a pump with 100% efficiency - which in the practial life is never true. An overall efficiency of 80 - 95% is common.
The equation above (1) can be modified to
PHP = q p / ((μ / 100) 1714) (2)
where
μ = overall efficiency (%)



