Condensate Generated in Cold Steam Pipes - Sizing of Steam Traps
When cold steam pipes are heated up they generate huge amounts of condensate that must be drained away from the pipe through steam traps - in Imperial Units.
When cold steam pipes are heated up they generate huge amounts of condensate that must be drained away from the pipe. It is important that the steam traps are designed to handle the start up load.
The diagram and table below can be used as a roughly estimate of the warm-up condensate load generated when the steam system is heated up.
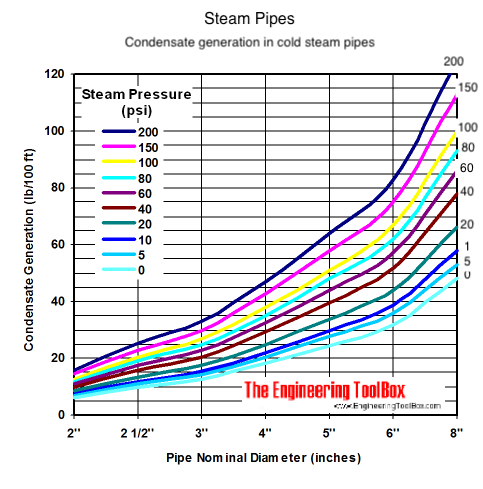
| Steam Gauge Pressure (psi) | Warm-Up Condensate Load (lb/100 ft) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe Size (inch) | |||||||||
| 2 | 2 1/2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | |
| 0 | 6.2 | 9.7 | 12.8 | 18.2 | 24.6 | 31.9 | 48 | 68 | 90 |
| 5 | 6.9 | 11 | 14.4 | 20.4 | 27.7 | 35.9 | 53 | 77 | 101 |
| 10 | 7.5 | 11.8 | 15.5 | 22 | 29.9 | 38.8 | 58 | 83 | 109 |
| 20 | 8.4 | 13.4 | 17.5 | 24.9 | 33.8 | 44 | 66 | 93 | 124 |
| 40 | 9.9 | 15.8 | 20.6 | 29.3 | 39.7 | 52 | 78 | 110 | 145 |
| 60 | 11 | 17.5 | 22.9 | 32.6 | 44 | 57 | 86 | 122 | 162 |
| 80 | 12 | 19 | 24.9 | 35.3 | 48 | 62 | 93 | 132 | 175 |
| 100 | 12.8 | 20.3 | 26.9 | 37.8 | 51 | 67 | 100 | 142 | 188 |
| 125 | 13.7 | 21.7 | 28.4 | 40 | 55 | 71 | 107 | 152 | 200 |
| 150 | 14.5 | 23 | 30 | 43 | 58 | 75 | 113 | 160 | 212 |
| 175 | 15.3 | 24.2 | 31.7 | 45 | 61 | 79 | 119 | 169 | 224 |
| 200 | 16 | 25.3 | 33.1 | 47 | 64 | 83 | 125 | 177 | 234 |
| 250 | 17.2 | 27.3 | 35.8 | 51 | 69 | 89 | 134 | 191 | 252 |
| 300 | 25 | 38.3 | 51 | 75 | 104 | 143 | 217 | 322 | 443 |
| 400 | 27.8 | 43 | 57 | 83 | 116 | 159 | 241 | 358 | 493 |
| 500 | 30.2 | 46 | 62 | 91 | 126 | 173 | 262 | 389 | 535 |
| 600 | 32.7 | 50 | 67 | 98 | 136 | 187 | 284 | 421 | 579 |
| 800 | 38 | 58 | 77 | 113 | 203 | 274 | 455 | 670 | 943 |
| 1000 | 45 | 64 | 86 | 126 | 227 | 305 | 508 | 748 | 1052 |
| 1200 | 52 | 72 | 96 | 140 | 253 | 340 | 566 | 833 | 1172 |
| 1400 | 62 | 79 | 106 | 155 | 280 | 376 | 626 | 922 | 1297 |
| 1600 | 71 | 87 | 117 | 171 | 309 | 415 | 62 | 1018 | 1432 |
| 1750 | 78 | 94 | 126 | 184 | 333 | 448 | 746 | 1098 | 1544 |
| 1800 | 80 | 97 | 129 | 189 | 341 | 459 | 764 | 1125 | 1584 |
This table is based on an ambient temperature of 70 oF. For an ambient temperature of 0 oF, the values should be increased with 15% at 1800 psi and up to 50% at 0 psi.
- 1 ft (foot) = 0.3048 m
- 1 psi (lb/in2) = 6,894.8 Pa (N/m2) = 6.895×10-2 bar
- 1 lb = 0.4536 kg



