Steam Pipes - Installation of Drip Legs
Properly draining steam pipes for condensate.
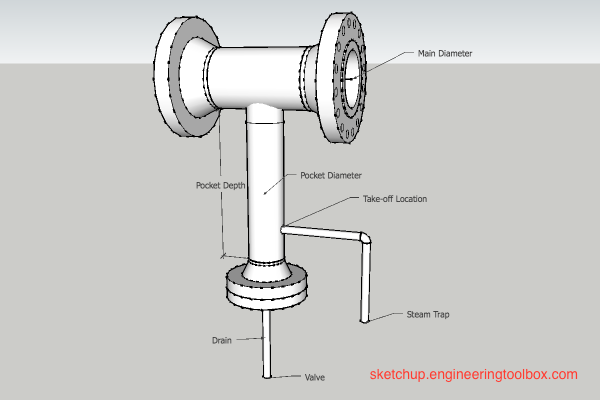
The 3D model above is made with sketchup.engineeringtoolbox.com
Condensate is generated in the steam pipes due to heat loss and due to energy required during system heat up. For the steam system to work properly it is important that the condensate is removed.
Steam traps for draining should be located
- on horizontal pipes - every 30 - 50 m (100 - 150 ft)
- in front of pressure reducing valves to avoid damaging the equipment
- in front of control valves to avoid damaging the equipment
- in front of normally closed valves to avoid building up condensate that may damage the system when accelerated
- at the bottom of vertical lines
- at the end of the steam line
Recommended Drip Leg Dimensions
| Main Diameter | Pocket Diameter | Pocket Depth | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | (in) | (mm) | (in) | (mm) | (in) |
| 50 | 2 | 50 | 2 | 700 | 28 |
| 80 | 3 | 80 | 3 | 700 | 28 |
| 100 | 4 | 100 | 4 | 700 | 28 |
| 250 | 10 | 150 | 6 | 700 | 28 |
| 500 | 20 | 250 | 10 | 700 | 28 |
Example - Drip Leg Dimensions
The recommended drip leg dimension for a 80 mm (3 in) steam pipe is 80 mm (3 in). The pocket depth should be 700 mm (28 in).
Related Topics
-
Steam and Condensate
Design of steam & condensate systems with properties, capacities, sizing of pipe lines, system configuration and more.
Related Documents
-
Condensate Generated in Cold Steam Pipes - SI Units
Huge amounts of condensate are generated when cold steam pipes are heated up must be drained from the pipes. -
Condensate Generated in Cold Steam Pipes - Sizing of Steam Traps
When cold steam pipes are heated up they generate huge amounts of condensate that must be drained away from the pipe through steam traps - in Imperial Units. -
Condensate Pipe Lines - Friction Resistance Imperial Units
Friction or major resistance in condensate pipe lines. -
Condensate Pipe Lines - Sizing
Flow and pressure loss in condensate return lines - SI Units. -
Condensate Pumping
High temperatures and danger of impeller cavitation is the major challenge for condensate pumping in steam systems. -
Insulated Steam Pipes - Condensate Generated
Heat loss from steam pipes generates condensate which must be drained from the system - imperial units. -
Insulated Steam Pipes - Condensate Generated (kg/h per 100m)
Heat loss from steam pipes generates condensate which must be drained from the system. -
Sizing Steam Pipes (lb/h)
Steam is a compressible gas where the capacity of a pipe line depends on the size of the pipe and the steam pressure. -
Steam - Gravity Return Condensate Pipes - Capacities
Max. capacities (lb/hour) in gravity condensate return lines. -
Steam Pipes - Sizing
Sizing of steam pipe lines - major and minor loss in steam distribution systems. -
Steam Trap Selection Guide
Steam trap selection guide - Float & Thermostatic, Inverted Bucket, Bimetal Thermostatic, Impulse and Thermodynamic Disc steam traps. -
Steam Traps - Safety Factors
Selection of steam traps and their safety factors.




