Ventilation Efficiency
The efficiency of a ventilation system may be related to temperature and/or pollution concentrations.
The efficiency of ventilation systems are in general related to
- temperatures, and/or
- pollution and contaminants concentrations
in supply air, room air and outlet air.
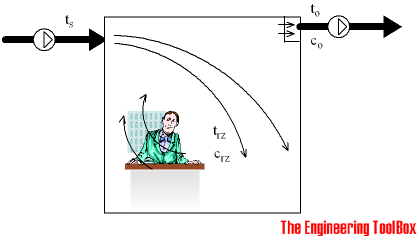
Temperature Efficiency
Temperature efficiency of a ventilation system can be calculated as
μ t = (t o - t s ) / (t rz - t s ) (1)
where
μ t = temperature efficiency
t o = outlet air temperature ( oC, oF)
t s = supply air temperature ( oC, oF)
t rz = room temperature in the residence zone - mean value ( oC, oF)
The potential efficiency of a system depends on the ventilation principle used.
Short Cut Ventilation
With "short cuts" the outlet temperature is close to the supply temperature and the ventilation efficiency approaches to zero.
Mixed Ventilation
With mixed ventilation the outlet temperature is close to the room temperature in the residential zone and the ventilation efficiency approaches to one.
Displacement Ventilation
With displacement ventilation the outlet temperature is higher than the temperature in the residence zone and in the supply air. The ventilation efficiency is higher (often much higher depending on the actual conditions) than one.
Piston Ventilation
Piston ventilation is an extreme variant of displacement ventilation. The efficiency is always higher than one.
Pollution Efficiency
Pollution or contaminant efficiency may calculated as
μv = c o / c rz (2)
where
μv = ventilation efficiency
c o = pollution concentration in the outlet air (kg/m3, lbm /ft3 )
c rz = pollution concentration in the air in the residence zone, mean value (kg/m3, lbm /ft3 )
The pollution or contaminant concentration in the outlet air can be expressed as
c o = q s / qv (3)
where
q s = pollution flow in the air (kg/s)
qv = outlet air flow (m3 /s)
The mean pollution concentration in the room can be expressed as
c rz = G / V (4)
where
c rz = pollution concentration in the room (kg/m3 )
G = total pollution in the room (kg)
V = volume of the room (m3 )
Short Cut Ventilation
With "short cuts" the pollution concentration in the outlet is less than in the air in the residential zone and the ventilation efficiency will approach to zero.
Mixed Ventilation
With mixed ventilation the outlet pollution concentration is close to the pollution concentration in the residential zone and the ventilation efficiency will approach to one.
Displacement Ventilation
With displacement ventilation the outlet pollution concentration is higher than the pollution concentration in the residence zone. The ventilation efficiency is higher (often much higher depending on the actual conditions) than one.
Piston Ventilation
Piston ventilation is an extreme variant of the displacement ventilation . The efficiency is always higher than one.
Related Topics
-
Ventilation Systems
Design of systems for ventilation and air handling - air change rates, ducts and pressure drops, charts and diagrams and more.
Related Documents
-
Comfort Environments - Selecting Ventilation System
A quick selection guide of ventilation system in comfort environments. -
Parts per Million - ppm
ppm - or parts per million - is commonly used as a unit of concentration. -
Ventilation Principles
Some commonly used ventilation principles - short cut, mixed air, displacement and piston principle.




