Electrical Formulas
Commonly used electrical formulas like Ohms Law and more.
Common electrical units used in formulas and equations are:
- Volt - unit of electrical potential or motive force - potential is required to send one ampere of current through one ohm of resistance
- Ohm - unit of resistance - one ohm is the resistance offered to the passage of one ampere when impelled by one volt
- Ampere - units of current - one ampere is the current which one volt can send through a resistance of one ohm
- Watt - unit of electrical energy or power - one watt is the product of one ampere and one volt - one ampere of current flowing under the force of one volt gives one watt of energy
- Volt Ampere - product of volts and amperes as shown by a voltmeter and ammeter - in direct current systems the volt ampere is the same as watts or the energy delivered - in alternating current systems - the volts and amperes may or may not be 100% synchronous - when synchronous the volt amperes equals the watts on a wattmeter - when not synchronous volt amperes exceed watts - reactive power
- kiloVolt Ampere - one kilovolt ampere - kVA - is equal to 1000 volt amperes
- Power Factor - ratio of watts to volt amperes
Ohm's Law Calculator
Add values for two parameters and the two others will be calculated. Delete the input for the values you want to calculate.
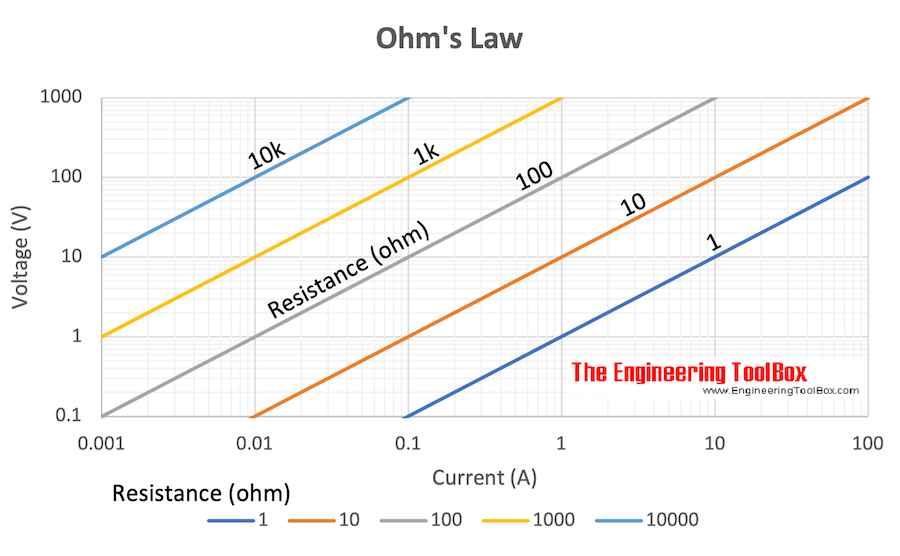
Electrical Potential - Ohm's Law
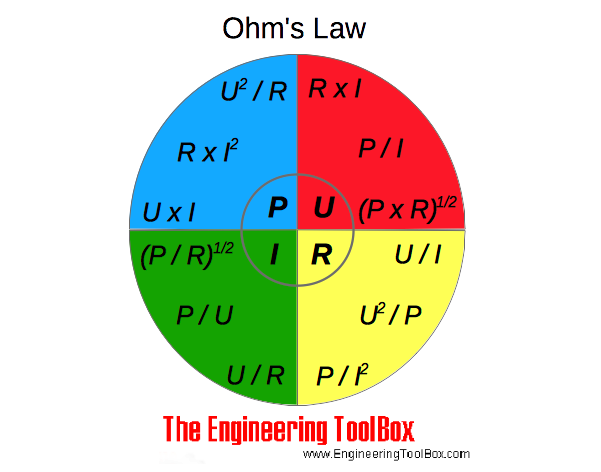
Ohm's law can be expressed as:
U = R I (1a)
U = P / I (1b)
U = (P R)1/2 (1c)
Electric Current - Ohm's Law
I = U / R (2a)
I = P / U (2b)
I = (P / R)1/2 (2c)
Electric Resistance - Ohm's Law
R = U / I (3a)
R = U2 / P (3b)
R = P / I2 (3c)
Example - Ohm's law
A 12 volt battery supplies power to a resistance of 18 ohms.
I = (12 V) / (18 Ω)
= 0.67 (A)
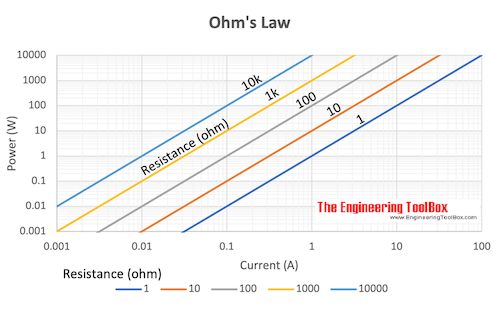
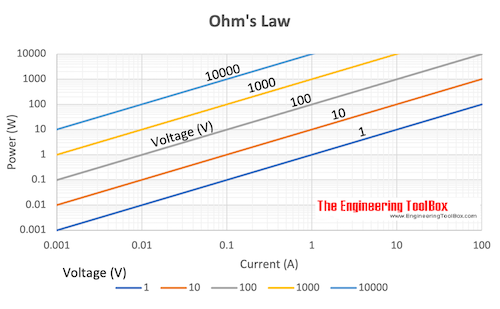
Electric Power
P = U I (4a)
P = R I2 (4b)
P = U2 / R (4c)
where
P = power (watts, W, J/s)
U = voltage (volts, V)
I = current (amperes, A)
R = resistance (ohms, Ω)
Electric Energy
Electric energy is power multiplied with time:
W = P t (5)
where
W = energy (Ws, J)
t = time (s)
Alternative - power can be expressed
P = W / t (5b)
Power is consumption of energy by consumption of time.
Example - Energy lost in a Resistor
A 12 V battery is connected in series with a resistance of 50 ohm. The power consumed in the resistor can be calculated as
P = (12 V)2 / (50 ohm)
= 2.9 W
The current through the resistor can be calculated as
I = (2.9 W) / (12 V)
= 0.24 A
The energy dissipated in 60 seconds can be calculated
W = (2.9 W) (60 s)
= 174 Ws, J
= 0.174 kWs
= 4.8×10-5 kWh
Example - Electric Stove
An electric stove consumes 5 MJ of energy from a 230 V power supply when turned on in 60 minutes.
The power rating - energy per unit time - of the stove can be calculated as
P = (5 MJ) (106 J/MJ) / ((60 min) (60 s/min))
= 1389 W
= 1.39 kW
The current can be calculated
I = (1389 W) / (230 V)
= 6 ampere
Electrical Motors
Electrical Motor Efficiency
μ = 746 Php / Pinput_w (6)
where
μ = efficiency
Php = output horsepower (hp)
Pinput_w = input electrical power (watts)
or alternatively
μ = 746 Php / (1.732 V I PF) (6b)
Electrical Motor - Power
P3-phase = (U I PF 1.732) / 1,000 (7)
where
P3-phase = electrical power 3-phase motor (kW)
PF = power factor electrical motor
Electrical Motor - Amps
I3-phase = (746 Php) / (1.732 VμPF) (8)
where
I3-phase = electrical current 3-phase motor (amps)