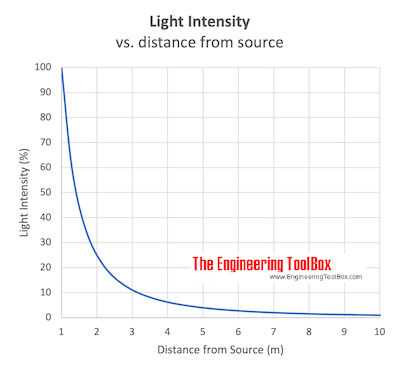
Optical Distance Law
Geometric dilution of light vs. distance.
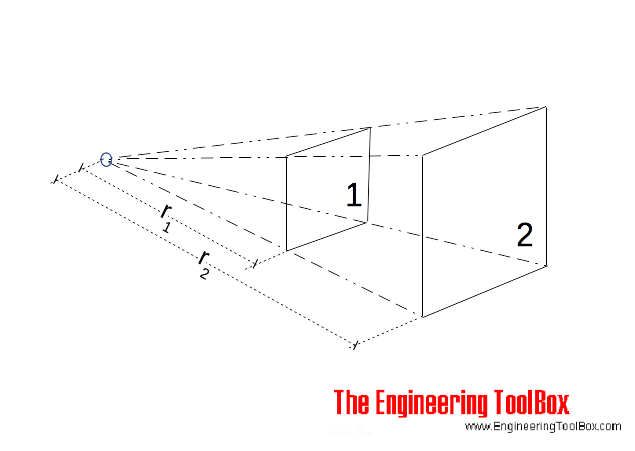
The illumination intensity on a surface is inversely proportional to the square of its distance from the light source and can be expressed as
E = Φ / d2 (1)
where
E = light intensity, illumination (lux, lumen/m2)
Φ = the quantity of light emitted by a lamp or a light source - luminous flux (lumen, lm)
d = distance from light source (m)
Since
E1 d12 = E2 d2 2
= constant (2)
(2) can be modified to
E1 / E2 = d2 2 / d12 (2b)
Example - Illumination Intensity from a Lamp at distance
The illumination intensity from lamp with luminance 10000 lumens at distance 2 m can be calculated with (1) as
E1 = (10000 lumens) / (2 m)2
= 2500 lux
The illumination intensity at distance 5 m can be calculated by modifying (2b) to
E2 = E1 d12 / d2 2
= (2500 lux) (2 m)2 / (5 m)2
= 400 lux
Cosine law of Illumination
E = (Φ / d2) cos(θ) (3)
where
θ = angle between light source vertical line and sight line