Charles' Law
Volume of an ideal gas vs. temperature.
Charles' law states that in a perfect gas where the mass and pressure is kept constant, the volume vary directly with the absolute temperature.
Charles' Law can be expressed as
V / T = constant (1)
or
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2 (1b)
where
V = volume (m3, ft3...)
T = absolute temperature (K, oR)
Example - Charles' Law
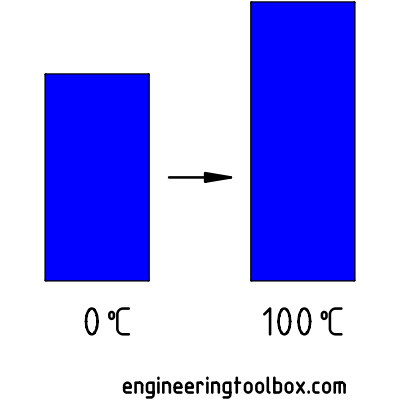
A gas occupies a volume of 2 liter at 0 oC . The volume it occupies at 100 oC can be calculated as
V2 = T2 V1 / T1
= (373 K) (2 liters) / (273 K)
= 2.73 (liters)