Piping Equations
Calculate cross-sectional areas, weight of empty pipes, weight of pipes filled with water, inside and outside surface areas.
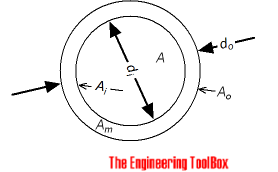
Cross Sectional inside Pipe Area
Cross-sectional inside area of a pipe can be calculated as
Ai = π (di / 2)2
= π di 2 / 4 (1)
where
Ai = cross-sectional inside area of pipe (m2, in2)
di = inside diameter (m, in)
Cross Sectional Pipe Wall Area
The cross-sectional wall area - or area of piping material - can be calculated as
Am = π (do / 2)2 - π (di / 2)2
= π (do 2 - di 2) / 4 (2)
where
Am = cross-sectional wall area of pipe (m2, in2)
do = outside diameter (m, in)
Weight of Empty Pipes
Weight of empty pipes per unit length can be calculated as
wp = ρm Am
= ρm (π (do / 2)2 - π (di / 2)2)
= ρm π (do2 - di2) / 4 (3)
where
wp = weight of empty pipe per unit length (kg/m, lb/in)
ρs = density of pipe material (kg/m3, lb/in3)
Weight of Liquid in Pipes
Weight of liquid in pipes per unit length can be calculated as
wl = ρl A
= ρl π (di / 2)2
= ρl π di2 / 4 (4)
where
wl = weight of liquid in pipe per unit length of pipe (kg, lb)
ρl = density of liquid (kg/m3, lb/in3)
Weight of Pipe filled with Liquid
Weight of pipe filled with liquid per unit length can be calculated as
w = wl + wp (5)
where
w = weight of pipe and liquid per unit length of pipe (kg, lb)
Outside Surface Area of Pipes
Outside surface area of steel pipes per unit length can be calculated as
Ao = 2 π (do / 2)
= π do (6)
where
Ao = outside area of pipe - per unit length of pipe (m2, in2)
Inside Surface Area of Pipes
Inside surface area of steel pipes per unit length can be calculated as
Ai = 2 π (di / 2)
= π di (7)
where
Ai = inside area of pipe - per unit length of pipe (m2, in2)
Related Topics
-
Dimensions of Pipes and Tubes
Pipe, tube and fittings sizes and dimensions. Inside and outside diameters, weights and more.
Related Documents
-
ANSI Schedule 40 Steel Pipes - Dimensions
Internal and external diameters, areas, weights, volumes and number of threads for ANSI schedule 40 steel pipes. -
Area Units Converter
Convert between units of area. -
Darcy-Weisbach Equation - Major Pressure and Head Loss due to Friction
The Darcy-Weisbach equation can be used to calculate the major pressure and head loss due to friction in ducts, pipes or tubes. -
Hazen-Williams Friction Loss Equation - calculating Head Loss in Water Pipes
Friction head loss (ftH2O per 100 ft pipe) in water pipes can be estimated with the empirical Hazen-Williams equation. -
Ice Loaded Pipelines
Ice coat weight on horizontal pipe lines. -
Manning's Formula and Gravity Flow
Calculate cross-sectional average velocity flow in open channels. -
Pipe and Tubing Formulas
Pipe and Tube Equations - moment of inertia, section modulus, traverse metal area, external pipe surface and traverse internal area - imperial units -
Pipe Weight Calculator
Weight calculating equation for steel pipes. -
Pipes - Fractional Equivalents
Fractional vs. decimal inches. -
Pipes - Nominal Wall Thickness
Nominal wall thickness of seamless and welded carbon and alloy steel pipes -
Pipes and Tubes - Water Content
Water content in steel pipes and copper tubes. -
Stainless Steel Pipes - Dimensions and Weights
Dimensions, wall thickness and weights of stainless steel pipes according to ASME B36.19 Stainless Steel Pipes. -
Welded Steel Pipes - Weights
Nominal weights of welded steel pipes ranging 26 - 60 inches.




